Security Insights
Security Predictions for 2026: What Every CISO Needs to Know
 By John Svazic
By John Svazic 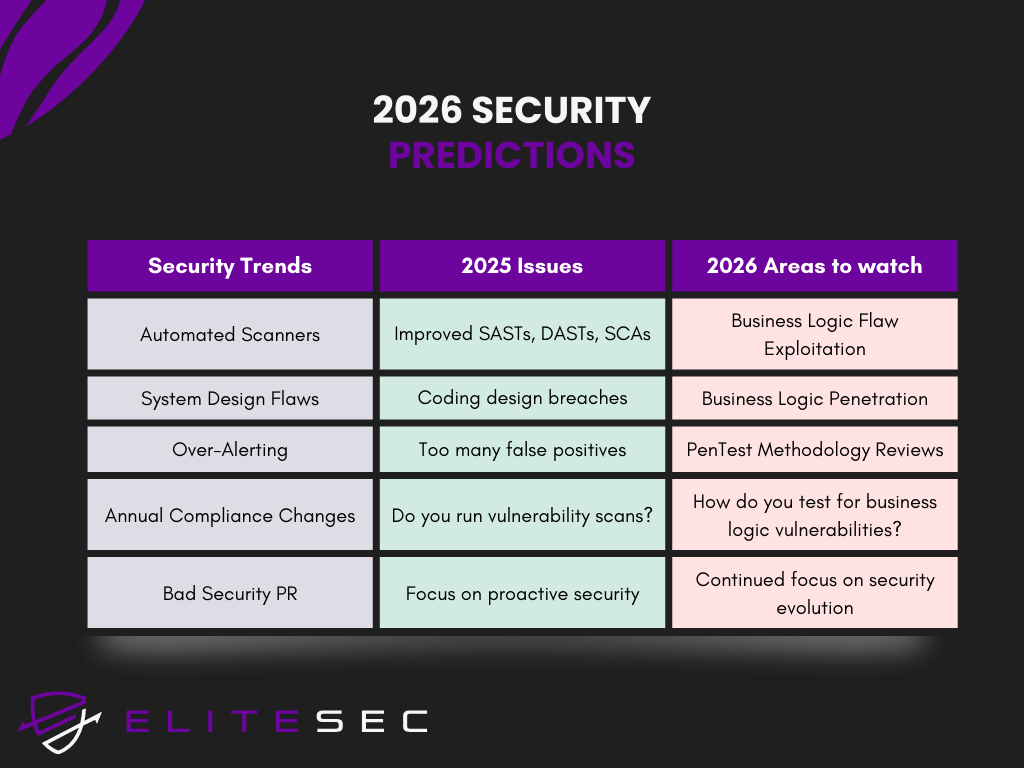
As we close out 2025 and head into 2026, the security landscape looks fundamentally different than it did 12 months ago. Three converging trends are reshaping how organizations must approach application security:
AI code generation reached mainstream adoption. GitHub Copilot, ChatGPT, and similar tools now write an estimated 40-60% of new code in production systems. This code is syntactically correct and passes automated scans—but often lacks critical business logic constraints.
Compliance requirements evolved beyond scanning. Mid-2025 updates to SOC 2 Trust Services Criteria, DORA technical standards, and cyber insurance questionnaires all added similar language: demonstrate business logic testing, not just vulnerability scanning. Scanner reports alone no longer satisfy auditors.
Breach patterns shifted to business logic. According to Microsoft’s 2025 Digital Defense Report and Google’s Threat Horizons analysis, the 2025 breaches that made headlines weren’t from unpatched CVEs. They were logic failures: payment flows allowing post-authorization amount changes, authentication systems validating only on page load, multi-tenant systems allowing cross-tenant data access through chained API calls.
Scanners detect pattern-matching problems. Business logic requires reasoning about what should never happen in a system—a fundamentally different challenge.
Five predictions for 2026
Based on these 2025 trends, here’s what’s coming in the next 12 months.
1. AI-generated code will lead to significant breaches
With AI tools now writing 40-60% of production code, we’re seeing a dangerous pattern emerge: AI generates code that implements “allow user to update record” without understanding implicit constraints like “only their own tenant’s records” or “only if payment hasn’t been processed.”
The prediction: In 2026, we’ll see breaches directly attributed to AI-generated code. The postmortems will reveal:
- Code that was syntactically correct and passed all automated tests
- Functionality that violated unstated business rules
- Security scanners that found no issues because technically, nothing was “wrong”
- Business logic failures that allowed unauthorized access or data manipulation
Why it matters: The real danger here is human judgment, not the tools themselves. When developers can produce code 10x faster with AI assistance, security training and awareness become exponentially more critical. Organizations need to invest in upskilling their teams to recognize when AI-suggested code violates business rules, understand the security implications of rapid development, and apply proper judgment before merging AI-generated code into production systems.
The bottleneck has shifted from “how fast can we write code?” to “how well do our developers understand what this code should never do?” Training programs, security awareness exercises, and validation processes become the critical defense layer.
2. Business logic testing becomes mandatory for compliance
The 2025 trend is clear: SOC 2 auditors shifted from accepting vulnerability scan reports to requiring evidence of business logic testing. DORA technical standards, updated cyber insurance questionnaires, and PCI DSS 4.0 all now reference testing for “chained exploit paths” and “business logic integrity.”
The prediction: By Q2 2026, you won’t be able to achieve these certifications without documented business logic testing:
- SOC 2 Type II (auditors will require specific testing artifacts)
- Cyber insurance above $5M limits (underwriters rejecting scanner-only evidence)
- Enterprise procurement (security questionnaires explicitly asking for human-led testing proof)
- PCI DSS 4.0 for payment processors (business logic testing for payment flows)
Why it matters: Q1 2026 brings annual insurance renewals and SOC 2 recertifications—a hard cutoff, not gradual evolution. Organizations showing up with only SAST/DAST reports will face delays, exclusions, or outright denials. The compliance goalposts have moved, and most organizations haven’t noticed yet.
3. Alert fatigue will drive security team attrition
The data from 2025 is damning: Splunk’s State of Security report found 46% of security professionals spend more time maintaining tools than defending their organization. Microsoft and Google research documented 18-28% productivity losses to false positive triage. Beyond inefficiency, teams face existential burnout.
When security teams face 47 “critical” alerts and 46 are false positives, they develop learned helplessness. Real vulnerabilities get triaged with the same “probably nothing” reflex as noise. The psychological toll is measurable and increasing.
The prediction: In 2026, security team attrition will correlate directly with alert volume. Organizations drowning in scanner noise will lose their best people to companies that prioritize signal over volume. We’ll see:
- Security professionals refusing roles at “high-alert-volume” organizations
- Exit interviews citing “constant false positive fatigue” as primary reason for leaving
- Industry shift from measuring “scans performed” to “validated findings resolved”
- Budget reallocation from scanning tools to human-validated triage and focused penetration testing
Why it matters: The cybersecurity talent shortage is already critical. Organizations that burn out their teams with tool maintenance and noise won’t be able to replace them. The competitive advantage goes to companies that prove their findings are validated and actionable—quality over quantity in both findings and team retention.
4. Legal and regulatory pressure will redefine “reasonable security measures”
2025 saw significant expansion of breach disclosure requirements: SEC cybersecurity rules, FTC Safeguards Rule updates, and state-level breach notification laws all now require disclosing what security measures were in place when breaches occurred. Combined with findings from the CrowdStrike 2025 Global Threat Report documenting the inadequacy of automated tools against sophisticated attacks, this creates increasing legal and regulatory pressure.
The prediction: In 2026, breach litigation and regulatory enforcement will increasingly scrutinize the quality and frequency of security testing. Discovery in breach cases will reveal:
- Gaps of 12-18+ months between penetration tests
- Testing limited to technical vulnerabilities, ignoring business logic
- Documented findings that were never remediated
- No retesting to validate fixes
Organizations relying solely on automated scanning will face harder questions in litigation, regulatory investigations, and insurance claims about whether they met “reasonable security measures” standards.
Why it matters: The legal definition of “reasonable security measures” is evolving to explicitly include regular, documented, human-led penetration testing with validated remediation. Boards need to shift from “Are we compliant?” to “Can we defend our testing program under legal scrutiny?” Insurance premiums will increasingly stratify based on testing documentation quality and frequency.
5. Demonstrable security testing becomes increasingly table stakes for enterprise sales
2025 showed a clear pattern: companies avoiding breaches weren’t those with the most scanning tools or biggest security budgets. They were organizations that focused testing on critical business flows and could demonstrate validated security posture to prospects and customers.
The prediction: Throughout 2026, enterprise buyers will increasingly require security proof beyond certifications. RFP security questionnaires will evolve to ask:
- “When was your last business logic penetration test?” (not “Do you run scans?”)
- “How do you validate AI-generated code for business logic correctness?”
- “Show evidence of continuous testing, not just annual audits”
- “Provide artifacts demonstrating human validation of critical workflows”
B2B SaaS companies that can’t provide this documentation will find themselves disqualified before pricing discussions even begin. SOC 2 certification remains essential, but the new competitive differentiator is provable, continuous security validation.
Why it matters: Enterprise buyers now expect vendors to prove security posture, not just claim compliance. Organizations treating security as checkbox theater will lose deals to competitors demonstrating continuous, validated testing programs. Security transitions from cost center to revenue enabler—the companies that can document their testing rigor win more enterprise contracts.
How to adapt your 2026 security strategy
Based on these predictions, here’s what needs to change in your 2026 security approach:
Shift budget from more tools to better validation. Stop adding scanners. Start investing in human-led penetration testing that validates business logic. Focus on validated proof that critical workflows can’t be subverted, not comprehensive scanning.
Document what should never happen. For every critical flow (authentication, payments, refunds, data export), explicitly document: “What should never be possible?” Then test whether those invariants actually hold. This documentation becomes your defensible security posture.
Plan for continuous testing, not annual audits. Every time authentication logic changes, payment workflows are updated, or new integrations are added, retest those specific areas. Business logic bugs resurface after code changes—annual testing no longer meets the need.
Prepare compliance evidence now. Q1 2026 brings SOC 2 audits and cyber insurance renewals. Auditors and underwriters will ask for human-validated penetration testing artifacts. If you don’t have them, expect delays, exclusions, or failed certifications.
Address AI-generated code risk. If developers are using Copilot, ChatGPT, or similar tools, implement validation processes. AI-suggested code needs human review for business logic correctness, not just syntactic validity. Consider engaging security consulting services to establish secure coding practices and review your development workflows.
Train your team on security awareness. As attack patterns shift to business logic exploitation, your entire team needs to understand what can go wrong. Gamified tabletop exercises help teams recognize social engineering, business logic abuse, and incident response protocols in realistic scenarios.
Implementation: What to do before Q1 2026 ends
Before your January board meeting:
- Document your three most critical business flows and what should never happen in each
- Review when your last human-led penetration test occurred and what it covered
- Identify gaps: Were business logic and chained exploits tested, or just technical vulnerabilities?
Before Q1 insurance renewal:
- Gather penetration testing artifacts that demonstrate human validation, not just scanner reports
- Ensure testing covered business logic, not just code quality
- If you lack these artifacts, schedule emergency penetration testing now
Before your next major release:
- Map handoff points where context and permissions might not be re-validated (API → queue → UI → third-party)
- Document business logic invariants: allowlists, balance checks, role-context rules
- Test whether these invariants can be violated through chained actions
- Conduct threat modeling sessions with security consulting experts to identify attack paths specific to your architecture
For AI-generated code:
- Require human review of all AI-suggested authentication, authorization, and payment logic
- Test AI-generated code for “technically valid but logically forbidden” behaviors
- Document which flows use AI-generated code so penetration testers know to focus there
How EliteSec helps you prepare for 2026
If these predictions concern you—and they should—here’s how we help organizations get ahead of these trends.
Business logic penetration testing that satisfies compliance requirements
We don’t just run scanners. Our CREST-accredited methodology focuses on what automated tools can’t detect: testing whether your business workflows can be subverted, whether legitimate actions can be chained into illegitimate outcomes, and whether your implicit business rules actually hold under adversarial pressure.
What you get:
- Human-led testing from start to finish—no hand-offs, no context loss
- Artifacts that auditors and insurers accept for SOC 2, DORA, and cyber insurance compliance
- Focus on critical flows: authentication, payments, refunds, data access, integrations
- Board-ready reporting that explains business impact, not just technical findings
Continuous validation with five free retests
Business logic vulnerabilities resurface after code changes. When you’re shipping weekly, annual penetration testing falls short. We include five free retests within 12 months so you can validate fixes and retest after significant changes to authentication, payment logic, or privilege systems.
This continuous validation model is what satisfies the new compliance requirements—and what will differentiate you in enterprise sales cycles.
AI-generated code security review
If your developers use GitHub Copilot, ChatGPT, or similar tools, we can identify which critical flows include AI-suggested code and specifically test for “technically valid but logically forbidden” behaviors. We document what should never happen in those flows, then validate whether AI-generated implementations actually prevent it.
Canadian data residency
For organizations with data residency requirements, all vulnerability findings and testing artifacts remain in Canadian jurisdiction. No US cloud providers, no cross-border data transit.
Beyond penetration testing
Preparing for 2026 requires more than just testing. We also offer:
- Cybersecurity Consulting for threat modeling, secure development practices, and security program reviews
- Gamified Tabletop Exercises to train your teams on incident response, social engineering awareness, and business logic attack patterns in realistic, engaging scenarios
Ready to prepare for 2026? Book a consultation to discuss your specific security posture, or download a sample penetration testing report to see what CREST-accredited business logic testing looks like.
– John
Sources
- Microsoft Digital Defense Report 2025 - Comprehensive analysis of global cybersecurity threats, trends, and the productivity impact of security operations.
- Google Cloud Threat Horizons Report H2 2025 - Research on cloud security challenges, alert overload, and evolving threat landscapes.
- CrowdStrike 2025 Global Threat Report - In-depth analysis of detection fidelity challenges, false positive rates, and velocity losses from alert churn.
- Splunk State of Security 2025 - Survey of over 2,000 security professionals revealing that 46% spend more time maintaining tools than defending their organization, with insights on SOC efficiency and alert fatigue.


